February 3, 2025
World Wetlands Day 2025 Theme/वर्ल्ड वेटलैंड्स डे 2025 थीम:
Why in News ?The theme for World Wetlands Day 2025 is “Protecting Wetlands for Our Common Future.” This theme underscores the urgency of bold action to protect these natural habitats for the welfare of all people, ensuring that future generations can continue to benefit from all that wetlands provide.
Significance of World Wetlands Day:
- World Wetlands Day is observed annually on February 2nd to commemorate the adoption of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands in 1971.
- The day aims to raise awareness about the vital role wetlands play in sustaining biodiversity, supporting livelihoods, and mitigating climate change.
- It serves as a reminder of the need for conservation and sustainable management of these ecosystems.
Convention on Wetlands:
- The Convention on Wetlands, known as the Ramsar Convention, is an international treaty adopted in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran. It provides the framework for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands worldwide.
- The convention emphasizes the ecological, cultural, economic, and scientific value of wetlands and encourages countries to designate wetlands of international importance, known as Ramsar Sites.
Wetlands in India & Ramsar Sites:
India has designated 89 Ramsar Sites as of January 2025, recognizing their international importance. These sites encompass a variety of wetland types, including freshwater lakes, coastal lagoons, and mangroves.
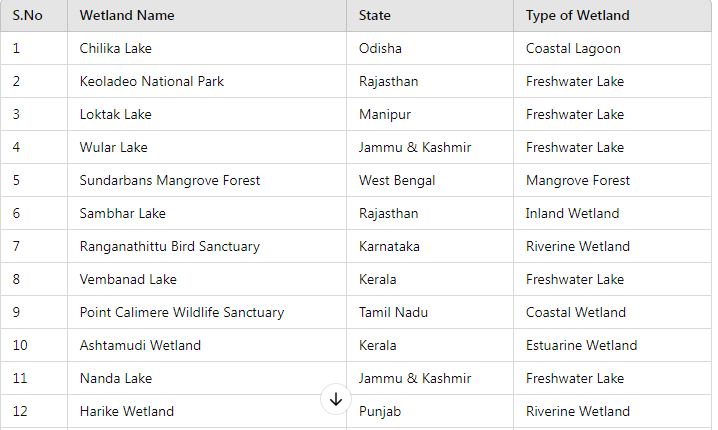
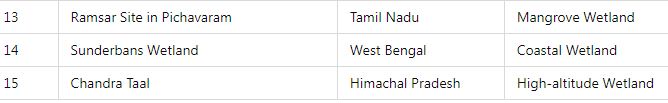
Categories of wetlands in India :
Freshwater Lakes and Rivers:
These wetlands include natural and man-made lakes, reservoirs, and rivers that are primarily freshwater.
Examples: Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan), Loktak Lake (Manipur).
Coastal Wetlands:
- Found along the coastlines, these include estuaries, tidal flats, and coastal marshes. They play a crucial role in protecting shorelines from erosion and act as nurseries for many marine species.
Examples: Chilika Lake (Odisha), Sundarbans Mangrove Forests (West Bengal).
Mangroves:
- Coastal forests found in intertidal zones, mainly in the deltas, and are characterized by salt-tolerant trees. Mangroves are crucial for biodiversity and coastal protection.
- Examples: Sundarbans Mangrove Forest (West Bengal), Pichavaram Mangroves (Tamil Nadu).
Coral Reefs:
- Marine ecosystems that are formed by coral polyps, which create a dense colony of calcium carbonate. They support diverse marine life and act as barriers for coastal protection.
- Examples: Lakshadweep Islands, Gulf of Mannar (Tamil Nadu).
Floodplains:
- These wetlands are located adjacent to rivers, and are periodically flooded by river waters. They play a role in groundwater recharge and nutrient cycling.
- Examples: Kolleru Lake (Andhra Pradesh), Tso Moriri Lake (Ladakh).
Wetland Conservation Measures in India:
India has taken several significant steps to conserve its wetlands, focusing on sustainable management, legislative frameworks, and community involvement. Some of the recent and ongoing initiatives are:
Ramsar Convention Implementation:
- Designation of Ramsar Sites: India has designated 89 wetlands as Ramsar Sites (as of 2025), recognizing their international importance and committing to their protection.
- Key Measures: Protection, sustainable management, and international collaboration to conserve biodiversity and ensure the ecological integrity of these sites.
National Wetland Conservation Programme (NWCP):
- Objective: Launched by the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC), the NWCP aims to conserve and manage wetlands in India.
Key Activities:
- Identifying and monitoring wetlands.
- Providing funding for wetland management plans and action plans.
- Raising awareness and building capacity for wetland conservation at the local level.
Wetland (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2017:
- Purpose: To regulate activities that affect wetlands and ensure their protection.
Key Provisions:
- Delineation of wetland boundaries.
- Prevention of encroachment and pollution.
- Restricting conversion of wetlands into non-wetland uses (e.g., agriculture or construction).
- Mandates for the preparation of integrated management plans for the protection of wetlands.
Integrated Management of Wetlands:
- Action Plans: Development of specific Integrated Management Plans (IMPs) for individual wetlands, aimed at achieving their conservation goals while balancing ecological and socio-economic needs.
- Community Participation: Local communities, especially those dependent on wetland resources, are actively involved in planning and managing these wetlands, ensuring that conservation does not hinder their livelihoods.
Wetland Conservation through Community Participation:
- Wetland Conservation Committees: Establishing local bodies, such as Wetland Management Committees, that work with local communities to ensure the sustainable use of wetland resources.
- Awareness Campaigns: NGOs and government organizations run programs to educate local populations about the importance of wetlands for biodiversity, flood control, and climate resilience.
National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and Wetland Conservation:
- Wetlands are integrated into the National Action Plan on Climate Change, recognizing their role in carbon sequestration, water management, and climate adaptation.
- Focus on wetland restoration to enhance resilience to climate change and reduce the impact of floods and droughts.
Research and Monitoring Initiatives:
- Remote Sensing and GIS Tools: These technologies are increasingly used to monitor wetland health, track changes in area, water quality, and biodiversity, and detect encroachments.
- Wetland Inventory: India has developed a national wetland inventory to gather data on the extent, condition, and significance of wetlands across the country.
State-Level Initiatives:
- Various states have formulated their own specific plans for the protection and restoration of wetlands.
- For instance, Tamil Nadu focuses on mangrove conservation, while Uttarakhand emphasizes high-altitude wetland conservation.
Increased Funding for Wetland Protection:
- Financial resources have been allocated to support wetland conservation efforts, including the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC) and other programs that address wetland-related issues.
Encouraging Private Sector Participation
- In some cases, private sector players are encouraged to invest in the restoration and conservation of wetlands, as part of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
These measures show India’s commitment to the sustainable management of wetlands, ensuring that they continue to provide vital ecosystem services while balancing conservation with community and economic needs.
वर्ल्ड वेटलैंड्स डे 2025 थीम:
वर्ल्ड वेटलैंड्स डे 2025 की थीम है “हमारे सामान्य भविष्य के लिए आर्द्रभूमियों का संरक्षण।” यह थीम इन प्राकृतिक आवासों के संरक्षण के लिए तात्कालिक और साहसिक कार्रवाई की आवश्यकता को रेखांकित करती है, ताकि भविष्य की पीढ़ियाँ आर्द्रभूमियों द्वारा प्रदान की जाने वाली सभी सेवाओं का लाभ उठा सकें।
वर्ल्ड वेटलैंड्स डे का महत्व:
• वर्ल्ड वेटलैंड्स डे हर साल 2 फरवरी को मनाया जाता है, जो 1971 में रामसर कन्वेंशन के अंगीकरण की वर्षगांठ को समर्पित है।
• यह दिवस आर्द्रभूमियों के जैव विविधता को बनाए रखने, आजीविका का समर्थन करने और जलवायु परिवर्तन को कम करने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका के बारे में जागरूकता बढ़ाने का उद्देश्य है।
• यह आर्द्रभूमियों के संरक्षण और उनके सतत प्रबंधन की आवश्यकता की याद दिलाता है।
आर्द्रभूमि कन्वेंशन:
आर्द्रभूमि कन्वेंशन, जिसे रामसर कन्वेंशन भी कहा जाता है, 1971 में ईरान के रामसर में अपनाया गया एक अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संधि है। यह संधि आर्द्रभूमियों के संरक्षण और सतत उपयोग के लिए एक रूपरेखा प्रदान करती है। यह आर्द्रभूमियों के पारिस्थितिकीय, सांस्कृतिक, आर्थिक और वैज्ञानिक महत्व पर जोर देती है और देशों को अंतर्राष्ट्रीय महत्व की आर्द्रभूमियों को रामसर स्थल के रूप में नामित करने के लिए प्रोत्साहित करती है।
भारत में आर्द्रभूमियाँ और रामसर स्थल:
भारत ने जनवरी 2025 तक 89 आर्द्रभूमियों को रामसर स्थल के रूप में नामित किया है, जो उनके अंतर्राष्ट्रीय महत्व को मान्यता प्रदान करती हैं। ये स्थल विभिन्न प्रकार की आर्द्रभूमि श्रेणियों में आते हैं, जैसे ताजे पानी की झीलें, तटीय लैगून, और मंग्रोव।
भारत में आर्द्रभूमियों की श्रेणियाँ:
- ताजे पानी की झीलें और नदियाँ:
- इन आर्द्रभूमियों में प्राकृतिक और कृत्रिम झीलें, जलाशय और नदियाँ शामिल हैं, जो मुख्य रूप से ताजे पानी की होती हैं।
- उदाहरण: केओलादेओ नेशनल पार्क (राजस्थान), लोकतक झील (मणिपुर)
- तटीय आर्द्रभूमियाँ:
- ये आर्द्रभूमियाँ तटरेखाओं के साथ पाई जाती हैं, जिनमें मुहाने, ज्वारीय मैदाने और तटीय दलदल शामिल हैं। ये तटों को कटाव से बचाने और कई समुद्री प्रजातियों के लिए प्रजनन स्थलों के रूप में कार्य करती हैं।
- उदाहरण: चिलिका झील (ओडिशा), सुंदरबन मंग्रोव वन (पश्चिम बंगाल)
- मंग्रोव:
- ये तटीय वन हैं जो इंटरटाइडल क्षेत्रों में पाए जाते हैं और खारा सहन करने वाले पेड़ों से बने होते हैं। मंग्रोव जैव विविधता और तटीय सुरक्षा के लिए महत्वपूर्ण होते हैं।
- उदाहरण: सुंदरबन मंग्रोव वन (पश्चिम बंगाल), पिचावरम मंग्रोव (तमिलनाडु)
- कोरल रीफ्स:
- ये समुद्री पारिस्थितिक तंत्र हैं जो कोरल पॉलीप्स द्वारा निर्मित होते हैं, जो कैल्शियम कार्बोनेट की एक घनी कॉलोनी बनाते हैं। ये समुद्री जीवन का समर्थन करते हैं और तटीय सुरक्षा के लिए अवरोधक के रूप में कार्य करते हैं।
- उदाहरण: लक्षद्वीप द्वीप समूह, गुल्फ ऑफ मन्नार (तमिलनाडु)
- बाढ़ के मैदान:
- ये आर्द्रभूमियाँ नदियों के पास स्थित होती हैं और नियमित रूप से नदी के पानी से बाढ़ग्रस्त हो जाती हैं। ये भूजल पुनर्भरण और पोषक तत्वों के संचलन में मदद करती हैं।
- उदाहरण: कोल्लेरू झील (आंध्र प्रदेश), त्सो मोरीरी झील (लद्दाख)
भारत में आर्द्रभूमि संरक्षण उपाय:
भारत ने अपने आर्द्रभूमियों के संरक्षण के लिए कई महत्वपूर्ण कदम उठाए हैं, जिनमें सतत प्रबंधन, विधायी ढांचा और समुदाय की भागीदारी पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया गया है। कुछ हाल की और निरंतर चल रही पहलों में शामिल हैं:
- रामसर कन्वेंशन का कार्यान्वयन
• रामसर स्थल की नामकरण: भारत ने 89 आर्द्रभूमियों को रामसर स्थल के रूप में नामित किया है (2025 तक), जो उनके अंतर्राष्ट्रीय महत्व को मान्यता देता है और उनके संरक्षण का संकल्प करता है।
• मुख्य उपाय: जैव विविधता के संरक्षण, सतत प्रबंधन और पारिस्थितिकीय अखंडता बनाए रखने के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग। - नेशनल वेटलैंड कंजरवेशन प्रोग्राम (NWCP)
• उद्देश्य: यह कार्यक्रम पर्यावरण, वन और जलवायु परिवर्तन मंत्रालय द्वारा आर्द्रभूमियों के संरक्षण और प्रबंधन के लिए शुरू किया गया है।
• मुख्य गतिविधियाँ:
• आर्द्रभूमियों की पहचान और निगरानी।
• आर्द्रभूमि प्रबंधन योजनाओं और कार्य योजनाओं के लिए वित्तीय सहायता प्रदान करना।
• आर्द्रभूमि संरक्षण के लिए स्थानीय स्तर पर जागरूकता बढ़ाना और क्षमता निर्माण करना। - वेटलैंड (कंजरवेशन एंड मैनेजमेंट) रूल्स, 2017
• उद्देश्य: यह नियम आर्द्रभूमियों को प्रभावित करने वाली गतिविधियों को नियंत्रित करता है और उनके संरक्षण को सुनिश्चित करता है।
• मुख्य प्रावधान:
• आर्द्रभूमि की सीमाओं का निर्धारण।
• अतिक्रमण और प्रदूषण को रोकना।
• आर्द्रभूमियों का कृषि या निर्माण जैसी गैर-आर्द्रभूमि उपयोग में रूपांतरण रोकना।
• आर्द्रभूमियों के संरक्षण के लिए एकीकृत प्रबंधन योजनाओं का निर्माण। - आर्द्रभूमि संरक्षण में समुदाय की भागीदारी
• आर्द्रभूमि प्रबंधन समितियाँ: स्थानीय समुदायों के साथ मिलकर आर्द्रभूमि संसाधनों का सतत उपयोग सुनिश्चित करने के लिए आर्द्रभूमि प्रबंधन समितियों का गठन किया गया है।
• जागरूकता अभियान: गैर सरकारी संगठन (NGOs) और सरकारी संगठन आर्द्रभूमियों के महत्व पर स्थानीय आबादी को शिक्षित करने के लिए कार्यक्रम चलाते हैं। - जलवायु परिवर्तन पर राष्ट्रीय कार्य योजना (NAPCC) और आर्द्रभूमि संरक्षण
• आर्द्रभूमियाँ जलवायु परिवर्तन के अनुकूलन, जल प्रबंधन और कार्बन स्रावण में अपनी भूमिका को पहचानती हैं।
• आर्द्रभूमि पुनर्स्थापन पर जोर देना, ताकि जलवायु परिवर्तन से संबंधित प्रभावों से निपटा जा सके और बाढ़ और सूखा के प्रभाव को कम किया जा सके। - अनुसंधान और निगरानी पहलों
• रिमोट सेंसिंग और GIS उपकरणों का उपयोग बढ़ा है, जो आर्द्रभूमि की स्थिति, जल गुणवत्ता और जैव विविधता की निगरानी करते हैं।
• आर्द्रभूमि सूची: भारत ने एक राष्ट्रीय आर्द्रभूमि सूची तैयार की है, जो देश भर में आर्द्रभूमियों के आकार, स्थिति और महत्व के बारे में जानकारी एकत्र करती है। - राज्य स्तरीय पहल
• विभिन्न राज्यों ने आर्द्रभूमियों के संरक्षण और पुनर्स्थापन के लिए अपनी विशिष्ट योजनाएँ बनाई हैं।
• उदाहरण स्वरूप, तमिलनाडु मंग्रोव संरक्षण पर ध्यान केंद्रित करता है, जबकि उत्तराखंड उच्च ऊंचाई वाली आर्द्रभूमियों के संरक्षण पर जोर देता है। - आर्द्रभूमि संरक्षण के लिए वित्तीय संसाधन
• आर्द्रभूमि संरक्षण प्रयासों के लिए वित्तीय संसाधन आवंटित किए गए हैं, जैसे राष्ट्रीय अनुकूलन कोष (NAFCC) और अन्य योजनाएँ जो आर्द्रभूमि संबंधित मुद्दों को संबोधित करती हैं। - निजी क्षेत्र की भागीदारी को बढ़ावा देना
• कुछ मामलों में निजी क्षेत्र को आर्द्रभूमियों के पुनर्स्थापन और संरक्षण में निवेश करने के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया गया है, यह उनके कॉर्पोरेट सोशल रिस्पॉन्सिबिलिटी (CSR) के तहत किया जाता है।
इन उपायों से यह स्पष्ट है कि भारत आर्द्रभूमियों के सतत प्रबंधन के लिए प्रतिबद्ध है, ताकि वे अपनी महत्वपूर्ण पारिस्थितिकी सेवाएं प्रदान करती रहें और संरक्षण और आर्थिक जरूरतों के बीच संतुलन बना रहे।
January 30, 2025
January 20, 2025
January 14, 2025
