November 6, 2023
Understanding Tellurium: Properties, Sources, and Applications
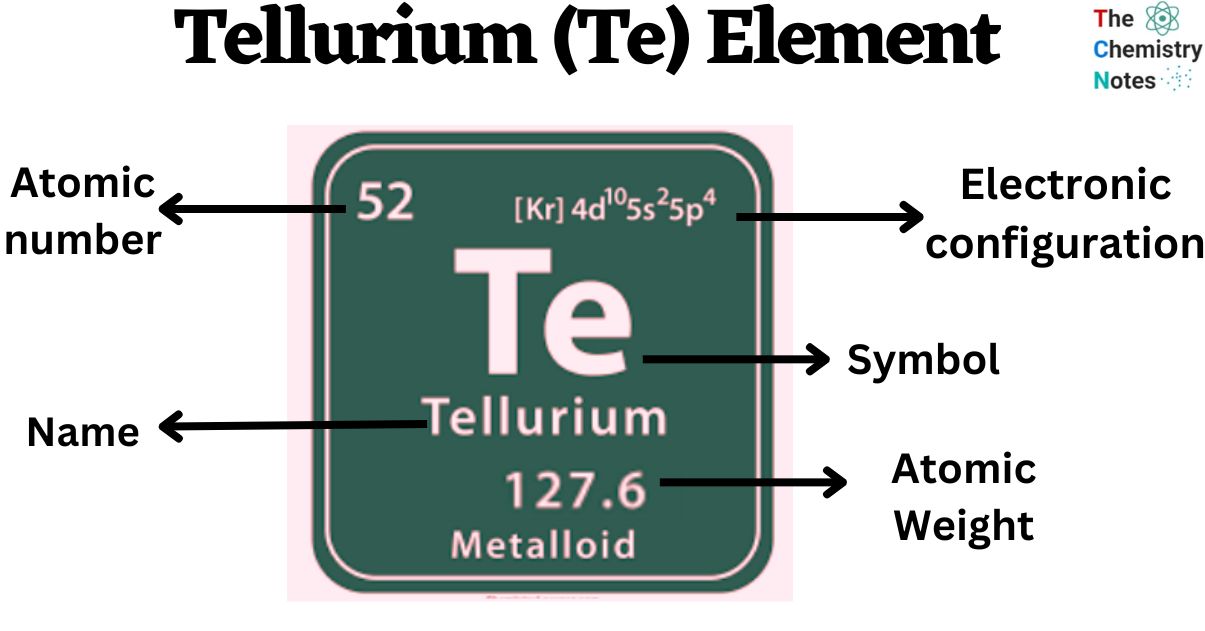
Introduction:
- Tellurium, with an atomic number of 52, is a unique semi-metallic element characterized by its lustrous, crystalline, and brittle silver-white appearance. Possessing properties of both metals and nonmetals, this element plays a significant role in various industrial applications. This article delves into the properties, natural sources, and diverse applications of tellurium.
Properties of Tellurium:
- Tellurium exhibits a semi-metallic nature, showcasing characteristics of both metals and nonmetals. When subjected to combustion, it emits a distinctive greenish-blue flame, resulting in the formation of tellurium dioxide. Additionally, tellurium is recognized as a semiconductor material with slight photosensitivity. Notably, it is one of the few elements known to readily combine with gold (Au), further expanding its versatility.
Sources of Tellurium:
- While occasionally found in a free state in nature, tellurium is more commonly encountered in combination with metals. Minerals such as calaverite (gold telluride, AuTe2) and sylvanite (silver-gold telluride) serve as prevalent sources of this element. Commercially, tellurium is obtained as a byproduct of electrolytic copper refining, contributing to its availability for various industrial applications.
Applications of Tellurium:
- Tellurium finds extensive use in a multitude of industries due to its unique properties. It is alloyed with copper and stainless steel to enhance their workability. In the realm of battery technology, it is added in minute quantities to lead, mitigating the corrosive effects of sulfuric acid and augmenting lead’s strength and hardness. Furthermore, tellurium acts as a vital colouring agent in ceramics, imparting distinctive hues. In the electronics sector, it is combined with cadmium and mercury to form photosensitive semiconductors, contributing to advancements in technology. Beyond this, tellurium plays roles in vulcanizing rubber, catalyzing petroleum cracking, and in the production of blasting caps for explosives.
Conclusion:
- Tellurium stands as a remarkable element with a diverse range of applications, owing to its distinctive properties. From enhancing the workability of metals to facilitating technological advancements in the electronics industry, tellurium’s contributions are substantial. Its availability as a byproduct of copper refining ensures its continued relevance in various industries. Understanding the properties and applications of tellurium provides valuable insights into its significance in modern industrial processes.
Daily Gist : The Hindu/Indian Express : 30 Jan 2025
January 30, 2025
Gist of editorial : the Hindu/ Indian Express/20 Jan 2025
January 20, 2025
Daily the Hindu/ Indian Express Editorial Gist: 14 Jan 2025
January 14, 2025
