February 20, 2024
Tribal Violence Erupts in Papua New Guinea’s Remote Highlands
In a recent development, a surge of tribal violence has claimed the lives of numerous men in the secluded highlands of Papua New Guinea.
Background on Papua New Guinea:
Geographical Overview:
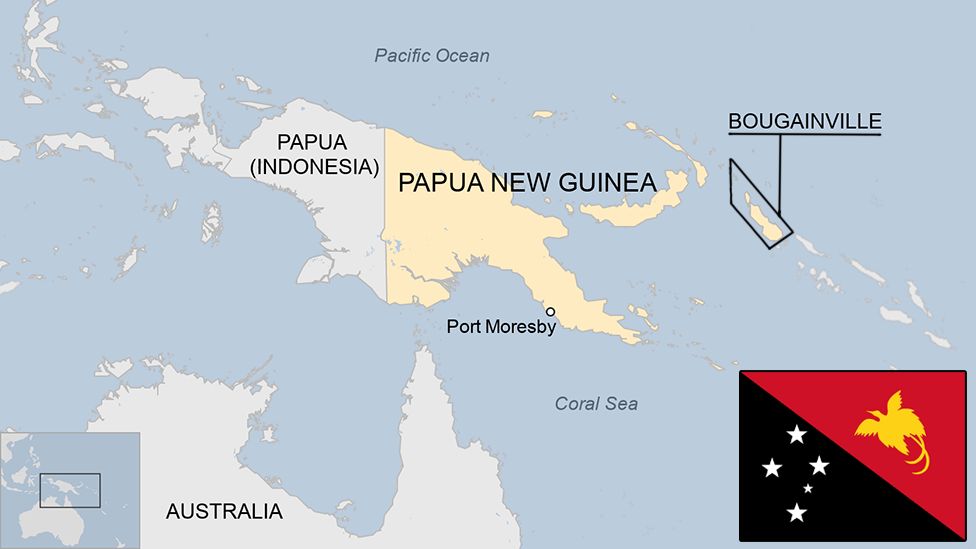
- Papua New Guinea is situated as an island nation in the southwestern Pacific region. It encompasses the eastern portion of New Guinea, the world’s second-largest island, along with several smaller offshore islands. Its neighboring countries include Indonesia to the west, Australia to the south, and the Solomon Islands to the southeast.
Capital and Terrain:
- The capital of Papua New Guinea is Port Moresby. Geographically, the country is characterized by its predominantly mountainous terrain, interspersed with low-lying plains in the southern part of New Guinea.
Population and Language:
- Over thousands of years, the islands comprising Papua New Guinea were inhabited by a diverse array of peoples, collectively known as Melanesians. The linguistic landscape of the nation is incredibly rich, boasting over 800 languages. While English serves as the primary language for governmental and commercial purposes, Tok Pisin is the most commonly spoken language in everyday interactions.
Religion and Governance:
- The majority of Papua New Guinea’s population identifies at least nominally as Christian. The country attained self-governance on December 1, 1973, and subsequently gained independence on September 16, 1975. Functioning as a constitutional monarchy within the Commonwealth, Papua New Guinea recognizes the British monarch, represented by a governor-general, as the head of state, while the Prime Minister serves as the head of government.
- In light of the recent surge in tribal violence, authorities in Papua New Guinea are facing renewed challenges in maintaining peace and stability, particularly in the remote highland regions.
Daily Gist : The Hindu/Indian Express : 30 Jan 2025
January 30, 2025
Gist of editorial : the Hindu/ Indian Express/20 Jan 2025
January 20, 2025
Daily the Hindu/ Indian Express Editorial Gist: 14 Jan 2025
January 14, 2025