January 17, 2025
Daily Legal Current for PCS- J/APO/Judiciary : 17Jan 2025/8th Pay Commission/ What is Pay Commission?History of Pay commission/8वां वेतन आयोग/वेतन आयोग क्या है ?वेतन आयोग का इतिहास
8th Pay Commission:
Implementation Timeline:
- Expected Start Date: January 1, 2026.
- Formation of Commission: Likely to be constituted by mid-2024, 18 months before implementation.
**2. Fitment Factor:
- Definition: A multiplier applied to the current basic pay to calculate the revised salary.
- 7th Pay Commission Factor: 2.57 (raised minimum basic pay from ₹7,000 to ₹18,000).
- 8th Pay Commission Projections: Fitment factor between 2.28 to 2.86.
- Minimum basic pay could increase from ₹18,000 to ₹41,000 to ₹51,480, depending on the exact factor.
**3. Pay Matrix:
- Definition: A tabular structure mapping salaries for different positions and seniority levels.
- Impact of 8th Pay Commission:
- Updated to reflect revised salaries.
- Example:
- Pay Matrix Level 1 employee (₹18,000 basic pay) could see a rise to ₹41,000 with a 2.28 fitment factor.
4. Salary Structure:
- Components:
- Basic Pay: Calculated by applying the fitment factor to current pay.
- Allowances: Include DA, HRA, TA, and others, recalculated based on new basic pay.
- Gross Salary: Total of basic pay and allowances.
- Example Calculation:
- Basic Pay: ₹41,000 (fitment factor 2.28).
- DA: 70% (₹28,700).
- HRA: 24% (₹9,840).
- Gross Salary: Approximately ₹79,540.
5. Pension Revisions:
- Minimum Pension Increase:
- From ₹9,000 under the 7th Pay Commission to approximately ₹20,500 with a 2.28 fitment factor.
6. Key Considerations:
- Economic Factors: Inflation, fiscal conditions, and government policies will influence final recommendations.
- Stakeholder Inputs: Employee unions and other stakeholders’ views will be taken into account.
- Proportional Revisions: Increments for all pay levels based on the updated matrix and fitment factor.
7. Anticipated Benefits:
- For Employees:
- Significant improvement in financial well-being.
- Revised salaries aligned with current economic realities.
- For Pensioners:
- Enhanced minimum pension to ensure financial security.
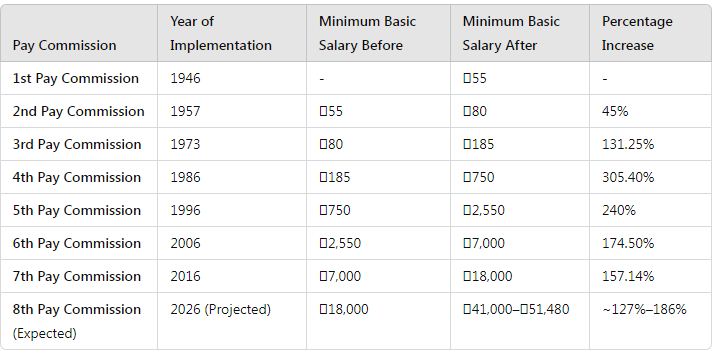
History of Pay Commissions in India
- Objective: To review and revise the salary structure of Central Government employees and pensioners, ensuring their pay aligns with economic conditions and inflation.
- Established By: The Central Government; recommendations are advisory and not binding.
Key Pay Commissions and Their Impact:
- 1st Pay Commission (1946):
- Focus: Post-independence salary structure for government employees.
- Key Outcome: Minimum basic salary fixed at ₹55 per month.
- Inflation Impact Considered: None, as inflation wasn’t a significant factor at the time.
- 2nd Pay Commission (1957):
- Focus: Address disparities between senior and junior employees.
- Key Outcome: Basic pay revised to ₹80 per month.
- 3rd Pay Commission (1973):
- Focus: Impact of inflation.
- Key Outcome: Realignment of salary with inflation trends and economic growth.
- 4th Pay Commission (1986):
- Focus: Modernizing the salary structure.
- Key Outcome: Basic pay increased significantly; the system of allowances introduced.
- 5th Pay Commission (1996):
- Focus: Balancing government finances and employee welfare.
- Key Outcome:
- Minimum basic pay increased to ₹2,550 per month.
- Pension reforms introduced.
- 6th Pay Commission (2006):
- Focus: Simplification of pay structures.
- Key Outcome:
- Introduction of the Pay Band system and Grade Pay.
- Minimum basic pay raised to ₹7,000.
- Increased allowances and pensions.
- 7th Pay Commission (2016)
- Focus: Rationalization of salary structure.
- Key Outcome:
- Introduction of the Pay Matrix system, replacing the Pay Band and Grade Pay system.
- Minimum basic pay increased to ₹18,000.
- Fitment factor of 2.57 introduced.
- 8th Pay Commission (Expected 2026)
- Focus: Aligning with contemporary economic conditions.
- Key Projections:
- Fitment factor of 2.28 to 2.86.
- Minimum basic pay expected to rise to ₹41,000–₹51,480.
Key Related Committees:
- Anomalies Committees:
- Formed after Pay Commissions to address discrepancies in recommendations.
- Focus on anomalies between different pay levels or employee categories.
- Koshyari Committee:
- Focused on improving pensions for defense personnel under the One Rank One Pension (OROP) scheme.
- Shetty Commission:
- Addressed salary revisions for judicial staff.
- N.K. Singh-led Finance Commission (15th):
- Examined pay structures in light of fiscal discipline and government expenditure.
What is Pay commission ?
- A Pay Commission is a body established by the Central Government to review and suggest revisions to the salary structure of its employees.
- It operates under the Department of Expenditure within the Ministry of Finance.
- Pay Commissions are typically formed every 10 years, with the first one constituted in 1946. Since India’s independence, seven Pay Commissions have been established.
- The most recent Pay Commission, the 7th Pay Commission, was formed in 2014, and its recommendations were implemented in 2016. Currently, central government employees and pensioners receive their salaries based on these recommendations.
It is important to note that the government is not obligated to accept the Pay Commission’s recommendations. The government retains the discretion to accept, reject, or modify the proposals as it deems fit.
कार्यान्वयन समय-सीमा:
प्रत्याशित प्रारंभ तिथि: 1 जनवरी, 2026।
आयोग का गठन: 2024 के मध्य तक होने की संभावना, कार्यान्वयन से 18 महीने पहले।
2. फिटमेंट फैक्टर:
परिभाषा: वर्तमान मूल वेतन पर लागू किया जाने वाला एक गुणक, जिससे संशोधित वेतन की गणना की जाती है।
- 7वें वेतन आयोग का फैक्टर: 2.57 (मूल वेतन ₹7,000 से ₹18,000 तक बढ़ा)।
- 8वें वेतन आयोग का अनुमान: फिटमेंट फैक्टर 2.28 से 2.86 के बीच।
- न्यूनतम मूल वेतन: ₹18,000 से बढ़कर ₹41,000 से ₹51,480 तक हो सकता है, फिटमेंट फैक्टर पर निर्भर करता है।
3. वेतन मैट्रिक्स (Pay Matrix):
परिभाषा: विभिन्न पदों और वरिष्ठता स्तरों के लिए वेतन का टेबल प्रारूप।
- 8वें वेतन आयोग का प्रभाव: वेतन को अपडेट कर संशोधित वेतन दिखाया जाएगा।
- उदाहरण:
- पद स्तर 1 का कर्मचारी (₹18,000 मूल वेतन): 2.28 फिटमेंट फैक्टर के साथ ₹41,000 तक बढ़ सकता है।
4. वेतन संरचना (Salary Structure):
घटक:
- मूल वेतन (Basic Pay): वर्तमान वेतन पर फिटमेंट फैक्टर लागू कर गणना।
- भत्ते (Allowances): डीए, एचआरए, टीए आदि, नए मूल वेतन के आधार पर पुनःगणना।
- सकल वेतन (Gross Salary): मूल वेतन और भत्तों का कुल योग।
- उदाहरण गणना:
- मूल वेतन: ₹41,000 (फिटमेंट फैक्टर 2.28)।
- डीए (महंगाई भत्ता): 70% (₹28,700)।
- एचआरए (गृह किराया भत्ता): 24% (₹9,840)।
- सकल वेतन: लगभग ₹79,540।
5. पेंशन संशोधन (Pension Revisions):
न्यूनतम पेंशन में वृद्धि:
- 7वें वेतन आयोग के तहत ₹9,000 से बढ़कर 2.28 फिटमेंट फैक्टर के साथ लगभग ₹20,500।
6. प्रमुख विचार (Key Considerations):
- आर्थिक कारक: महंगाई, राजकोषीय स्थिति और सरकारी नीतियां अंतिम सिफारिशों को प्रभावित करेंगी।
- हितधारकों के इनपुट: कर्मचारी संघ और अन्य हितधारकों के विचारों को ध्यान में रखा जाएगा।
- आनुपातिक संशोधन: अद्यतन मैट्रिक्स और फिटमेंट फैक्टर के आधार पर सभी वेतन स्तरों में वृद्धि।
7. अपेक्षित लाभ (Anticipated Benefits):
कर्मचारियों के लिए:
- वित्तीय स्थिति में उल्लेखनीय सुधार।
- वेतन संशोधन मौजूदा आर्थिक परिस्थितियों के अनुरूप।
पेंशनधारकों के लिए:
- न्यूनतम पेंशन में वृद्धि से वित्तीय सुरक्षा।
भारत में वेतन आयोगों का इतिहास:
उद्देश्य: केंद्रीय सरकारी कर्मचारियों और पेंशनधारकों के वेतन संरचना की समीक्षा और संशोधन, ताकि उनका वेतन आर्थिक परिस्थितियों और महंगाई के अनुरूप हो।
स्थापना: केंद्रीय सरकार द्वारा; सिफारिशें सलाहकारी होती हैं, बाध्यकारी नहीं।
मुख्य वेतन आयोग और उनका प्रभाव:
1. प्रथम वेतन आयोग (1946):
- फोकस: स्वतंत्रता के बाद सरकारी कर्मचारियों के वेतन की संरचना।
- प्रमुख परिणाम: न्यूनतम मूल वेतन ₹55 प्रति माह।
2. द्वितीय वेतन आयोग (1957):
- फोकस: वरिष्ठ और कनिष्ठ कर्मचारियों के बीच असमानता।
- प्रमुख परिणाम: मूल वेतन ₹80 प्रति माह।
3. तृतीय वेतन आयोग (1973):
- फोकस: महंगाई का प्रभाव।
- प्रमुख परिणाम: वेतन को महंगाई और आर्थिक वृद्धि के अनुरूप पुन: निर्धारित किया गया।
4. चतुर्थ वेतन आयोग (1986):
- फोकस: वेतन संरचना का आधुनिकीकरण।
- प्रमुख परिणाम: मूल वेतन में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि; भत्तों की प्रणाली शुरू।
5. पंचम वेतन आयोग (1996):
- फोकस: सरकारी वित्त और कर्मचारी कल्याण में संतुलन।
- प्रमुख परिणाम:
- न्यूनतम मूल वेतन ₹2,550 प्रति माह।
- पेंशन सुधार।
6. छठा वेतन आयोग (2006):
- फोकस: वेतन संरचना का सरलीकरण।
- प्रमुख परिणाम:
- पे बैंड सिस्टम और ग्रेड पे की शुरुआत।
- न्यूनतम मूल वेतन ₹7,000।
7. सातवां वेतन आयोग (2016):
- फोकस: वेतन संरचना का युक्तिकरण।
- प्रमुख परिणाम:
- पे मैट्रिक्स प्रणाली की शुरुआत।
- न्यूनतम मूल वेतन ₹18,000।
- फिटमेंट फैक्टर 2.57।
8. आठवां वेतन आयोग (प्रत्याशित 2026):
- फोकस: समकालीन आर्थिक परिस्थितियों के साथ तालमेल।
- प्रमुख अनुमान:
- फिटमेंट फैक्टर 2.28 से 2.86।
- न्यूनतम मूल वेतन ₹41,000–₹51,480।
संबंधित प्रमुख समितियां:
- अनॉमलीज़ कमेटी (Anomalies Committees):
- वेतन आयोगों के बाद सिफारिशों में विसंगतियों को दूर करने के लिए गठित।
- कोश्यारी समिति:
- ओआरओपी (One Rank One Pension) योजना के तहत रक्षा कर्मियों की पेंशन में सुधार।
- शेट्टी आयोग:
- न्यायिक कर्मचारियों के वेतन संशोधन।
- एन.के. सिंह वित्त आयोग (15वां):
- राजकोषीय अनुशासन और सरकारी व्यय के संदर्भ में वेतन संरचनाओं की जांच।
वेतन आयोग क्या है ?
वेतन आयोग एक ऐसा निकाय है जिसे केंद्रीय सरकार द्वारा अपने कर्मचारियों के वेतन ढांचे की समीक्षा और संशोधन की सिफारिश करने के लिए स्थापित किया जाता है। यह वित्त मंत्रालय के अंतर्गत व्यय विभाग के अधीन काम करता है।
महत्वपूर्ण तथ्य:
- स्थापना अंतराल: वेतन आयोग आमतौर पर हर 10 साल में गठित किए जाते हैं।
- पहला वेतन आयोग: 1946 में गठित किया गया।
- स्वतंत्रता के बाद: भारत में अब तक सात वेतन आयोग बनाए गए हैं।
- सातवां वेतन आयोग: 2014 में गठित हुआ, और इसकी सिफारिशें 2016 में लागू की गईं।
- वर्तमान स्थिति: केंद्रीय सरकार के कर्मचारी और पेंशनभोगी वर्तमान में 7वें वेतन आयोग की सिफारिशों के आधार पर वेतन प्राप्त कर रहे हैं।
- सिफारिशें बाध्यकारी नहीं: सरकार के लिए वेतन आयोग की सिफारिशों को स्वीकार करना अनिवार्य नहीं है।
- सरकार सिफारिशों को स्वीकार, अस्वीकार या संशोधित करने का अधिकार रखती है।
