November 1, 2023
Cloud Seeding Experiment Boosts Rainfall in Solapur by 18%
Introduction:
- Solapur, a city known for its limited rainfall due to its geographical location on the leeward side of the Western Ghats, recently witnessed a significant breakthrough in weather modification. Through a cloud seeding experiment, the city experienced an impressive 18% increase in rainfall. This achievement holds promise for regions facing water scarcity or drought conditions. In this article, we will delve into the details of the experiment, the technique of cloud seeding, its effectiveness, and the potential implications for water management.
Cloud Seeding: A Weather Modification Technique
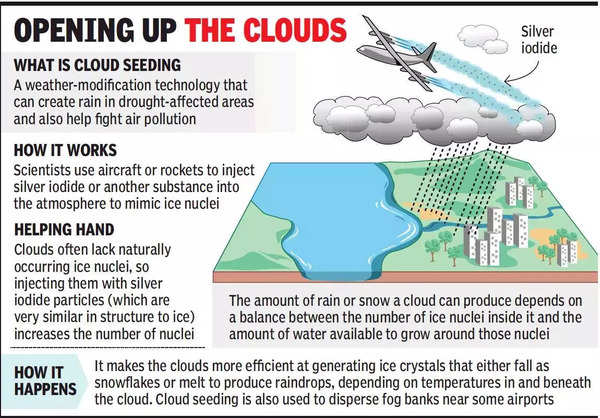
- Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique aimed at enhancing precipitation. The primary objective is to increase rainfall or snowfall in areas struggling with water scarcity or drought. This is achieved by introducing seeding agents, which can include substances like silver iodide, calcium chloride, potassium iodide, sodium chloride, among others, into suitable clouds. These clouds are typically convective in nature, exhibiting moisture and vertical motion.
Methods of Dispersion and Environmental Impact
- Cloud seeding can be implemented using various methods of dispersion, including aircraft, rockets, ground-based generators, and drones. Importantly, this technique is generally considered safe, with minimal environmental impact.
The CAIPEEX Experiment: A Breakthrough in Rainfall Augmentation
- The Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX phase-4) was a pioneering initiative that focused on investigating the efficacy of hygroscopic seeding in deep convective clouds. The results were nothing short of remarkable. Two hours after cloud seeding, an additional 8.67mm of rainfall was recorded, equating to a staggering 867 million litres of augmented water availability.
Significance of the Experiment
- The CAIPEEX experiment holds immense significance, particularly in the context of India’s growing burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs). Informed consumer choices and food safety are paramount in combating this issue, and the experiment’s success in enhancing rainfall could play a crucial role.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Key Findings
- The research also conducted a thorough cost-benefit analysis of cloud seeding, estimating the cost of producing water through this technique at 18 paise per litre. The study involved a randomized seeding experiment, selecting 276 convective clouds, with 150 subjected to seeding and 122 serving as the control group. The criteria for seeding included clouds with significant liquid water content, indicative vertical motion, and depth exceeding one kilometre. Calcium chloride flares were the chosen seeding agent, ensuring optimal dispersion and entry into growing clouds.
Implications and Future Prospects
- While cloud seeding alone may not be a complete solution to droughts, it has the potential to contribute significantly to rainfall augmentation. This 18% increase in rainfall could partially address water requirements in affected regions. Additionally, the potential for cost reduction, particularly through the use of indigenous seeding aircraft, could make cloud seeding a more accessible and sustainable option.
High-Resolution Numerical Model for Targeted Seeding
- The study has also developed a high-resolution numerical model that can aid stakeholders in identifying target locations, suitable clouds for seeding, and effective strategies for enhancing rainfall. This model represents a significant step forward in the science of weather modification.
Conclusion:
- The success of the CAIPEEX experiment in Solapur marks a significant advancement in weather modification through cloud seeding. This breakthrough not only showcases the potential of cloud seeding as an effective strategy for enhancing rainfall, especially in regions with suitable conditions, but also highlights its cost-effectiveness. As India grapples with water scarcity and the burden of non-communicable diseases, innovations like cloud seeding offer hope for a more sustainable and water-secure future.
Daily Gist : The Hindu/Indian Express : 30 Jan 2025
January 30, 2025
Gist of editorial : the Hindu/ Indian Express/20 Jan 2025
January 20, 2025
Daily the Hindu/ Indian Express Editorial Gist: 14 Jan 2025
January 14, 2025
